A-D
A
Airdrop : An airdrop is a free distribution of small quantities of a new crypto currency, sent to different users in the blockchain community.
All-in : Investing your entire capital on one asset. A technique strongly not recommended for beginners.
Altcoin : The term “Altcoin” or alternative coin is used to describe all the currencies other than Bitcoin. E.g. : Ethereum, Litecoin, Binance Coin…
Altcoin Season: Period with an upward trend where altcoins overperform against Bitcoin.
Fundamental Analysis : Analysis based on the overall functioning of a project and on what it brings as advantages/disadvantages to the market.
Technical Analysis (TA) : In-depth analysis conducted to evaluate investments and identify trading opportunities by analyzing trends gathered from a chart.
Arbitrage : Trading strategy in which an asset is bought then immediately sold on a different exchange platform. The goal is to make a certain profit by exploiting the price gap.
51% Attack : A 51% attack is an attack that aims at blockchains called “Proof of Work” (POW) or “Proof of Stake” (POS), the goal of this attack is to corrupt / alter the blockchain’s history.
Asic (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) : An ASIC miner is a device that uses microprocessors with the only purpose of mining certain cryptocurrencies.
ATH (All Time High) : Highest price ever achieved on a crypto currency
ATL (All Time Low) : Lowest price ever achieved on a crypto currency.
B
Bag : Refers to the list of crypto currencies that a trader holds in his portfolio.
Bear : Representation of a downward position, sell position. This name refers to the way a bear fights its enemies. The term “Bearish” refers to a cryptocurrency with numerous downward signals.
Bear Market : Market with a downward trend. A Bear Market usually occurs after a period of euphoria during a Bullrun and can last for multiple months/years.


Bear Trap : Downside trap where the price of a digital asset performs a false downward signal.
BearWhale : A person who sells their entire cryptocurrencies holdings and triggers a short-term dip on the market price.
Bid : The term “Bid” refers to the offer made by a user or a firm to buy an asset.
Bitcoin : Bitcoin is the very first of all crypto currencies to be published. It was developed in 2008 by the famous Satoshi Nakamoto and has since been the crypto with the biggest global capitalization.
💡 Click on this link to learn more about Bitcoin. 💡
Blockchain : A blockchain is a database type where numerous confidential information is stored electronically. A blockchain allows digital information to be registered and distributed, but not edited. Almost any transaction can be tracked and exchanged on a blockchain network, reducing the risk and cost for the users.
Break Even (BE) : Consist of placing your Stop Loss at the entry point of a trade. If this level of price is achieved, the position will close without making losses or profits.
Bull : Asset with an upward trend. The term “Bullish” refers to a market price with several upward signals.
Bull Market : An upward period for almost every cryptocurrency on the market.


Bull Trap : An upward trap where the market price of a crypto currency proceeds to a fake upward signal.
Burn : Method consisting in removing tokens from circulation, thus reducing the total supply of a crypto currency. The “burn” is a technique used by many exchanges, in order to add scarcity to their tokens, which usually leads to an increase in the price of the tokens.
C
Capital : Represents the total amount in a portfolio.
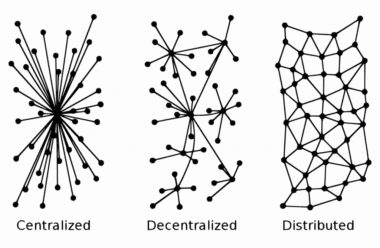
Centralization : Centralization refers to an organizational structure in which the decision-making power is given to a selected group of individuals. In numerous situations, top managers of a company have all the power.
Chart : Graph representing the price evolution of a digital asset.
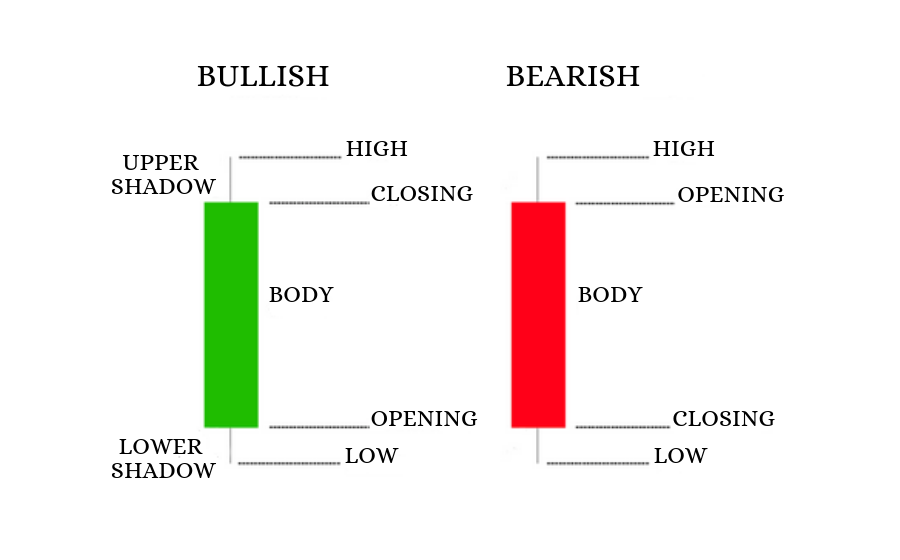
Japanese candlestick : Type of graph used in technical analysis representing the variations of a price.

CME (Chicago Mercantile Exchange) : One of the two main American futures markets.
Cold Wallet : A Cold Wallet is a physical private key storage that is not connected to the Internet (Ledger/Safepal). This solution highly limits the risks of hacking and is strongly recommended for storing crypto currencies in the long term.
Consolidation : Decrease or halt in buying pressure. A consolidation marks the indecision of traders after a sharp rise of a crypto currency price. Although this can lead to a short-term decrease, a consolidation by no means marks the end of an upward trend, but just a stabilization before the stock price recovers.
Correction : Reversal of the trend after a relatively important upward/downward movement.
Coss Margin : Option that uses the totality of available funds in a portfolio, to avoid liquidating your positions. Example : In the case where you are positioned on a contract with a $100 investment and the price reaches your liquidation price, the cross margin will draw from your cryptocurrency balance to avoid closing your position completely. You can find this trading method on derivative contracts such as Binance Futures, PrimeXBT or Bybit.
Cryptography : Writing technique used to protect confidential messages through the use of encrypted phrases, secret codes or decryption keys. This method is mainly used in the military and computer fields.
Crypto currency : Decentralized technology that allows users to perform secure payments and store money without having to go through an intermediate such as a bank. Cryptocurrencies are based on a “Blockchain”, a network that manages itself, notably used to store and transmit numerous information.
D
dApps : Applications or softwares running on a decentralized computer system.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) : Entirely automated governance system, allowing the proper functioning of a Blockchain. DAOs work through a combination of diverse smart contracts that allow participants to take an equitable part in the decision-making processes within an organization.
Day Trading : Investment strategy where traders trade their cryptocurrencies over a short period of time, generally ranging from a few hours to a few days.
Decentralization : A decentralized system that, as opposed to centralization, does not rely on a single center of authority to enforce rules and maintain the proper functioning of a network.

DCA (Dollar Cost Averaging) : Investment strategy used by people willing to invest a predefined amount of money at regular intervals, repeating it for multiple months/years.
DeFi : Financial system developed on blockchain networks, entirely decentralized and accessible to all. DeFi applications do not need intermediaries or mediators. Most of them are built on the Ethereum network, which allows the development of decentralized software programs through the use of smart contracts.
DEX (Decentralized Exchange) : Decentralized exchange platform allowing the trading of crypto currency safely.
Dip : Lowest point during a downward movement. A Dip is most certainly one of the best opportunities to invest in a cryptocurrency and is therefore strongly sought by traders.
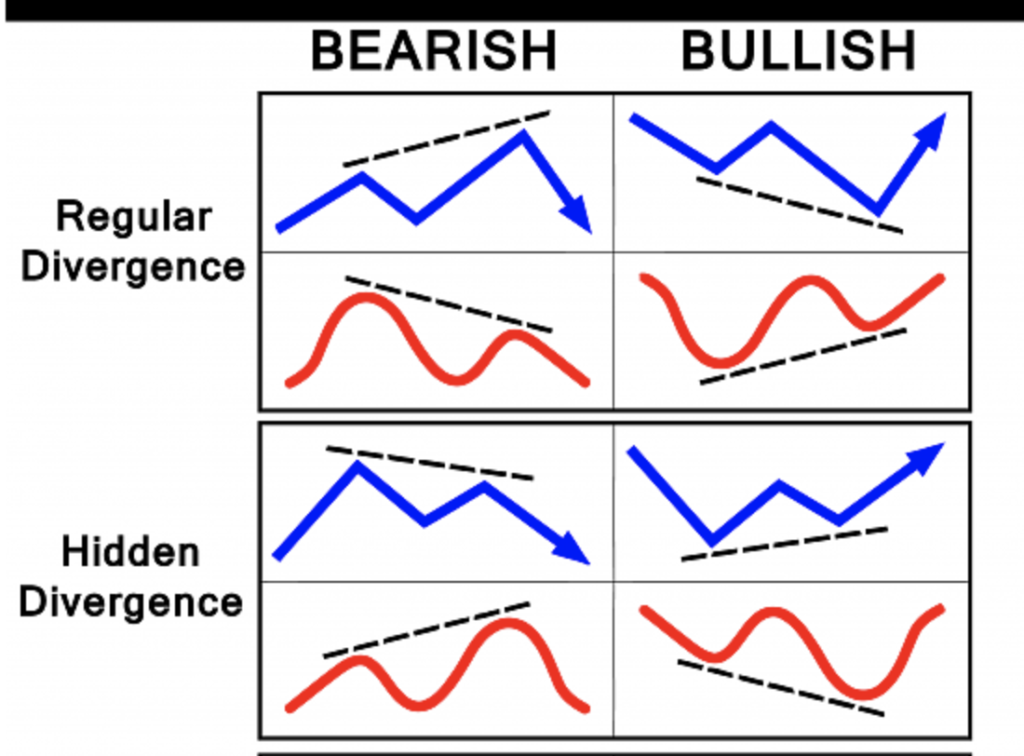
Divergence : Contradiction between the price of an asset and the information given by an indicator (RSI/MACD). In general, divergences announce huge reversals of upward and downward trends.

Doge Coin : Developed in 2013 by Billy Markus, Doge Coin is a crypto currency founded by a meme issued by the community, representing a Shiba Inu (dog breed). DOGE is now ranked 8th with a total capitalization of about $22 billions.
💡 Click on this link to learn more about Doge Coin. 💡
Dump : Downward movement with a very high intensity.
E-H
E
ERC-20 : Tokens used and developed solely on the Ethereum platform.
Ethereum : Ethereum is a peer-to-peer (P2P) monetary protocol distributed for smart contracts and decentralized applications. Its native token is ether (ETH), it is mainly used as a payment method for transaction fees and as a collateral for borrowing ERC-20 tokens in the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector.
Exchange : Exchange platform for crypto currencies. E.g. : Binance, FTX, Coinbase…
Exit Scam : Type of scam where a platform decides to seize the entirety of funds it has collected and never resurface. One of the biggest Exit Scam is the one carried by Bitconnect, grabbing several hundred million dollars.
F
Fee : Fees charged when a digital asset goes up/down.
Fomo : Expression referring to an investor who bets on an asset because of fear of missing a great deal. Fomo triggers the irrational increase of a crypto currency in the short term, usually followed by a brutal correction.
Fiat : Fiduciary currency that is legal tender, backed by a government and used in the current economy. E.g. : euros, dollars…
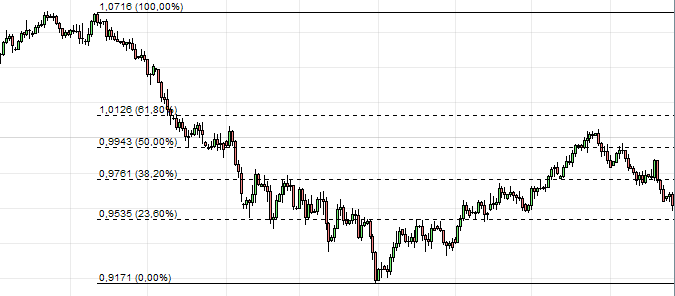
Fibonacci retracement : One of the most popular indicators in TA. It allows forecasting support areas and potential resistances when the trend of a digital asset changes. Never use only one indicator for your forecasts!

FUD : Negative or misleading news that can have a downward impact on the price of a digital asset.
Flash Crash : A stock market event in which the brutal increase in sales of an asset leads to the sudden fall of its price. E.g.: In 2010, a $4.1 billion order placed on the NYSE led to a loss of more than 1,000 points of its market index.
Flippening : Theoretical scenario in which Ethereum’s capitalization exceeds Bitcoin’s one.
Fork : Modification of the protocol of a blockchain network into two distinct chains. Forks occur when the software of different miners is misaligned. It is up to the miners to decide which blockchain to continue using.
Funding Fee : A trader is exposed to financing rate when taking a position on a derivative contract (futures). When the funding is positive, Longs pay to keep their position open and Shorts get paid. In contrast, when funding is negative, Shorts pay to keep their position open and Longs get paid.
Futures : Contract offering numerous investment tools that are not available in the Spot market.
G
Gains : Bet won as a result of a winning investment by a trader.
Gap : Variation in price between the closing and opening of a market, leading to an absence of transaction at these price levels.
Gas : Gas is a virtual unit principally dedicated to the validation and confirmation of transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. It refers to the computing effort required to execute operations.
GitHub : The biggest hosting platform for code and development of software programs worldwide. Most of the developers share their project progress on GitHub, where users can also ask their questions.
GPU (Graphical Processing Unit) : Computer technology found in graphics cards. GPU’s perform complex tasks to ensure the good rendering of a video game. They are also adapted for the mining of certain crypto currencies.
H
Hack : Computer hack that consists of stealing a maximum of information, data and money in the form of digital currencies or cryptocurrencies.
Halving : Event where the rewards per confirmed block made by miners are divided by two. For now, the Bitcoin network witnessed 3 “Halvings” : the first in November 2012, the second in July 2016 and the last one to date, in May 2020.
Hard Fork : Radical change of a network protocol in which a blockchain is divided in two parts. Hard forks are major events and are generally released to the community of a crypto currency well in advance. Example : Hard Fork of the Bitcoin blockchain in 2017 which gave birth to the Bitcoin Cash (BCH) project.
Hardware Wallet : Physical wallet allowing the storage of private keys in a fully secured computer device (E.g. : Ledger, Safepal…)
Hot Wallet : Virtual wallet allowing the sending and storage of crypto-assets with ease. Unlike “Cold Wallets”, hot wallets are connected to an internet network and are thus more exposed to hacking risks. This solution is preferable for the storage of crypto currencies in the short/medium term.
Harsh rate : Term used to describe the computing power of a crypto currency network. The Harsh rate is measured in units of hash/second, which represents the computing power per second that can be performed.
Higher High (HH) : A high point higher than the previous one.
Higher Low (HL) : A low point lower than the previous one.
Hold : Holding onto digital assets for the long term, regardless of price variations. This strategy is generally rewarded thanks to the deflation of the current crypto currency market.
I-M
I
Isolated Margin : Trading option that allows the management of each position independently. Unlike Cross Margin, isolated margin is a more secure method that prevents the liquidation of the totality of the funds on a wallet.
Inflation : Loss of the value of a currency, which means the general increase of prices in the market.
ICO (Initial Coin Offering) : Launching offer allowing investors to buy the first tokens put on sale by any project.
ITO (Initial Token Offering) : Similar to the ICO, ITO’s are more centered on offering tokens with intrinsic utility in the form of software or use in an ecosystem.
Invest : Allocating a certain amount of money on a digital/financial asset.
K
KYC (Know Your Customer) : Security device that verifies personal data and identity of customers. KYC is a mandatory step on most platforms in order to fight against money laundering and terrorism (AML-FT).
L
Lambo : The term “Lambo” is a meme initiated by the community. It refers to the luxury car that investors “symbolically” want to buy in case they become rich thanks to their investments.
Ledger : French company founded in 2014 that offers its own range of physical wallets (hardware wallets). You can store a very large number of private keys in it safely.
Access to the Ledger store through this link
Leverage effect : Trading instrument that allows to artificially increase the size of an investment/stake, without increasing market exposure. (Not recommended for beginners).
Lightning Network : A second layer technology that tackles the extensibility and scalability issues of the bitcoin network. The Lightning Network allows for faster, cheaper and easier transactions to validate.
Liquidation : Total loss of the amount invested in a digital asset.
Liquidity : The ease with which a crypto currency can be bought and sold without impacting the global market price. The more liquidity a market has, the easier it will be to buy/sell on it.
Long : Invest in the price increase of an asset by using a leverage effect.
Lower High : A higher high, lower than the previous one.
Lower Low : A lower low, lower than the previous one.
M
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) : A very popular indicator used in technical analysis. The MACD represents the trend that shows the relationship between two moving averages of the price of a digital asset. The MACD is calculated by subtracting the 26 period exponential moving average (EMA) from the 12 period one. In case where the two averages are about to cross, it is very likely that the trend is going to turn around. Never use only one indicator for your forecasts !

Margin Call : A margin call is sent if the market evolves in the opposite direction compared to a completed transaction. This reminder allows a trader to add additional funds in order to avoid the liquidation of his open position.
Margin Trading : Trading method that consists in borrowing funds from a broker to trade. While this practice allows you to boost your gains, it also exposes you to greater losses.
Market Cap : Represent the total capitalization of a digital asset.
Market Maker : Market Maker. Person/institution that contributes to ensuring enough liquidity in the markets, meaning a sufficient volume of trades so that transactions can be carried out in transparency.
Market Order : Type of buy or sell order that is immediately executed at the best possible market price. Note that you will pay fees as a Taker, meaning that you are taking liquidity from the market.
Masternodes : The Masternodes (“master nodes”) are powerful computer servers that perform critical tasks within an ecosystem. They are mainly used to ensure the security and efficiency of transactions on a blockchain network.
MetaMask : Online storage solution for digital assets. Only requires to install the extension available on Google Chrome, and then add the asset you want to store.
Mineur : A miner is a computer whose role is to validate transactions on a blockchain network, in exchange for a certain amount of crypto currencies.
Minting : Computer process of validating information, creating a new block and recording this information in the blockchain. This method is performed by users using a blockchain at a Proof of Stake (PoS) network.
Money-Management : Management of your digital asset wallet. It is very important for a trader to have a great management of his capital, in order to avoid making as many unthought decisions.
Moving Average : Indicator based on the average price of an asset, very often used in technical analysis. The moving average is a great mean of assessing the dynamic and confirming the current trend of a crypto currency. Never use only one indicator for your forecasts!
N-Q
N
Nodes : The nodes are micro-servers performing essential tasks within a blockchain network.
NFT (Non-Fungible Token) : An NFT is a unique token or a token with very limited supply. NFTs are purchased to be held for several years, so that they gain in value.
Nominators : Nominators perform major tasks within a blockchain network that uses the NPoS (nominated proof-of-stake) consensus algorithm.
O
OCO (One Cancel The Other) : Refers to an order that automatically cancels the previous one. If you place an OCO order and the first instruction is performed, the other one will be immediately cancelled. Very useful to create right from the beginning your TP and SL.
Open Source : Adjective given to software programs that are developed according to the OSI principles, the Open Source Initiative. Being open source allows users to use, alter and change a software or a code, according to their needs.
Options : Future market.
Oracle : An oracle is a group of networks/applications allowing the digitalization of information coming from external sources other than the Blockchain (off-Chain) through smart contracts. It gives blockchains the capacity to interact with data coming from the external world.
Order Book : The order book displays in real time the buy and sell orders made on a futures contract.
OTC (Over The Counter) : A term that refers to a transaction made outside of an exchange, thereby limiting the impact on the price of an asset, especially if the OTC transaction remains secret.
P
Panic Buy/Sell : Situation where a trader buys/sells his position during an important variation of the price market, whether it increases or decreases. This happens generally to inexperienced traders who do not yet know how to manage their emotions.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) : A peer-to-peer network is a decentralized system allowing the exchange or sharing of information between multiple computers.
PnL (profit and loss) : The PnL represents the profits and losses accumulated between the opening and closure of a position.
Portfolio : Set of digital assets held by a trader.
Ponzi Scheme : A ponzi is a scam that promises investors very high rates of return with only very small risk. However, once the price of the asset reaches a certain level, the founders disappear with the totality of the funds raised. Traders are strongly advised to research a project before investing in it.
Private key : Algorithmic code for digital asset portfolio. In general, private keys are used as passwords or access code and must be kept in a safe place.
Pump : Upward movement with a very strong intensity.
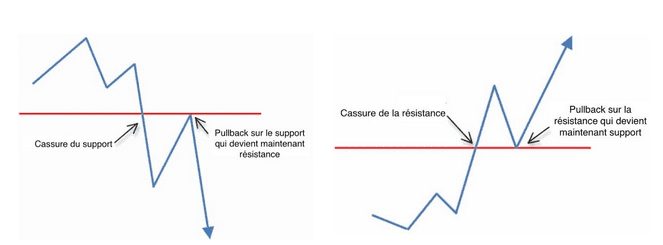
Pullback : Pause or temporary change in the trend of an asset. The market price returns to test a support area or resistance before going back to the initial trend. A Pullback often confirms the underlying trend and is a great entry point for traders.

Price Discovery : Discovery of a price. When the market price surpasses its ATH, it no longer has any reference point and is therefore in price discovery.
Proof of Stake (PoS) : Proof of Stake is a type of consensus mechanism used by blockchain networks, in order to maintain the integrity of a crypto currency, by preventing users from printing additional pieces that they have not earned. Furthermore, instead of using the computing power to participate in the development of a blockchain, the “PoS” algorithm allows participation according to the number of tokens made available to the network.
Proof of Work : First consensus system used by blockchains, in order to discourage malicious usage of computing power, such as sending spam or launching DDosS attacks. To create new blocks, miners must make their computing power available to solve mathematical equations.
💡 Click on this link to learn more about Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW). 💡
Pizza Day : Marks the first real-word (official) use of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. A Bitcoin miner located in Florida buys 2 pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins. At that time, 1 Bitcoin was worth between $0.003 and $0.004.
Q
QR Code : Virtual device that presents coded information in a black and white graphic pattern. In the world of crypto currencies, QR Code is mainly used to send and receive payments, in a much faster and automated way.
R-W
R
Range : A period of stagnation between two price levels. A range can last for a couple of weeks/months without the market price making any major upward or downward variation.

Risk/Reward (RR) : Ratio that represents the risk you take regarding the trade you are willing to make in an investment. Example: A RR of ⅕ for a bet of $10 means that you risk losing $10 for a potential gain of $50.
ROI (Return on Investment) : Abbreviation for “return on investment”, it refers to the relationship between net profit and investment cost. ROI gives a very strong indication on the performance and profitability of a trade.
RSI (Relative Strength Index) : The relative strength index (RSI) is an oscillator that measures the strength of an asset’s rise and fall over a predefined unit of time. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is an oscillator that measures the strength of an asset’s rise and fall over a predefined unit of time. The RSI is used to verify the strength and trend of a market. An asset is considered oversold if the RSI is below 30 and overbought if the RSI is above 70. Never use only one indicator for your forecasts !

S
Satoshi Nakamoto : Famous creator of Bitcoin whose identity is known by no one (or almost). Satoshi Nakamoto is the nickname used by the person who wrote the Bitcoin white book, in 2008.
Scalability : Capacity of a system/blockchain to adapt to the fluctuation of the amount of transactions and people using the network at the same time.
Scalping : Investment strategy where traders negotiate their assets in a very short period of time, going mainly between a few seconds to a few minutes.
Shitcoin : Crypto currency that has no viable project and a very uncertain future. Shitcoins generally bring no to a very low value to investors and are therefore not interesting for long-term investment.
Short : Invest on the fall of the price of an asset.
Sidechain : Sidechains are secondary blockchains that perform in parallel to the main blockchain. By allowing operations to be carried out on the periphery of the main blockchain, sidechains bring a lot in terms of scalability and functionality, they can for example reduce the time and cost of transactions.
Smart Contract : Smart contracts are computer protocols that are based on the Blockchain technology, in order to facilitate, verify and execute the negotiation or execution of a contract. Smart contracts allow users to carry out transactions in a transparent and conflict-free manner, while avoiding the services of a (centralized) intermediary.
Smart Contracts can also offer the possibility to developers to create and implement decentralized applications (dApps) on a blockchain network.
Spot Market : Public market where crypto currencies are traded for immediate settlement. It contrasts with future contracts, in which the settlement is expected later.
Spread : A spread can have multiple meanings in finance. Fundamentally, they all refer to the difference between the buy price (Ask) and the sell price (Bid) of a digital asset. For example : If the buy price of a crypto currency is $3.50 and the sell price is $3.35, the spread is therefore $0.15.
Stablecoin : Crypto currencies indexed to a stable value, such as the dollar. As the name indicates, Stablecoins have extremely low volatility, they are often used as a safer and reliable way to diversify.
Staking : The principle of staking is to lock an amount of crypto currencies into a wallet in order to get rewards, while contributing to the operations of a Blockchain. Staking is known to be used in numerous Blockchains using Proof of Stake (PoS) as the main consensus.
Stop Limit : Stop Limit orders are triggered in two stages, the first at the stop price and the second at the limit price. You must first define a stop price which, once reached, instantly triggers the “limit” price previously set.
Stop Loss : The “stop loss” tool, more often called SL, is an order triggered when the price reaches the forecasted price. This allows to limit losses on an investment.
Support : Price level at which the buying force is stronger than the selling force. A support is achieved through the high density of buy orders placed at a specific location in the price of a cryptocurrency.
Swap : Functionality allowing users of a platform to trade easily a crypto currency for another, without going through the market.
Swingtrade : Open trade position opened for multiple days.
T
Take Profit (TP) : The “take profit” tool, also called TP, is a conditional order that allows you to secure gains and to take some profits in order to reduce your market exposure. The order is set manually, depending on the rewards objectives that a trader is willing to reach.
Testnet : Alternative blockchain used by developers for testing multiple protocols. For example : On June 24, 2021, an update of Ethereum was deployed on the Ropsten testnet, so that the developers could ensure that the different implemented modifications were functional.
To The Moon : Very common term in the world of crypto currencies referring to the lightning increase of an asset’s price.
Token : Digital asset tradable that has a particular use in a blockchain network.
Tokenomics : The abbreviation of Token and Economy, represents for a crypto project, the way the creation of tokens will be managed for the proper functioning of the project.
Total Supply : Amount of assets in circulation (available to buy) at a designated time. It refers to the amount of coins already distributed (or issued) subtracted to the total of coins burnt.
Trading Bot : Computer program designed to automate the trading of crypto currencies, in order to achieve daily returns. A Trading Bot reproduces the defined investment strategy set by a trader and thus avoids all the actions linked to emotions.
Trend : Refers to an upward/downward trend.
V
Volatility : Every cryptocurrency that knows frequent and major movements is said to be volatile because of its low capitalization.
Volume Profile : Indicator displaying the market activity at certain price levels. The volume profile allows to display the price areas that the price has been working for a long time and to identify the potential areas that price will work.

W
Whale : Term referring to a person or organization holding enough crypto currencies to impact the market price in the short term. For example : A big share of existing bitcoins on the market (around 40%) would be held by around 1,000 people (whales).
White Paper : Document where the totality of the information regarding a blockchain or whatever cryptographic project is written.
Withdraw : The withdrawal of a set invested sum.
Y
Yellow Paper : The yellow paper presents a crypto project on every of its technical aspects and characteristics. It is complementary to the white paper.
Yield Farming : Yield Farming consists of creating tokens through other tokens, by indirectly “borrowing” money to other users, while getting rewarded by receiving interests thanks to the transactions fees. Users give liquidity to DeFi protocols in Smart Contracts called “Liquidity Pools”.


