Web 3 has quickly become one of the most talked about terms in the cryptocurrency industry. Since 2021, interest in it has continued to grow and many projects now claim to participate in the construction of this famous Web 3.0. What does Web 3 really bring and how does it differ from Web 2?
- Introducing Web 3
- What does Web 3 bring?
- What are the limits of Web 3?
- Conclusion on Web3
Introducing Web 3
Why are we trying to move away from Web 2?
To better understand the Web 3 , we must first distinguish it from what is called the Web 2 . It’s the user-generated, social media-based version of the internet we’re all familiar with.
We have been using it for many years, it is a centralized Internet dominated by web giants such as Google, Amazon, Apple and many others, who offer their services in exchange for users’ personal data, used for commercial purpose.
One consequence of this system is the trust that users must place in these companies to ensure the integrity of their data thus entrusted. However, frequent data leaks, hacks, identity theft or the sale of data without consent are commonplace in Web 2.0.
This centralization has certainly provided a robust infrastructure for the Web and allowed billions of individuals to have access to it, but these centralized entities can also decide unilaterally to censor what they do not like.
Censorship is a very powerful tool for silencing unwanted comments. Whether it is to ensure the interests of a company or to comply with government requests, this can lead to abuses.
Depending on the behavior or the content of a user’s speeches, these companies managing these services have unilateral decision-making power , the control is in their hands. The Web2 is thus dominated by these centralized entities, so freedom is relative .

Figure 1: Web 2.0 giants
These Web 2.0 giants, such as GAFA to name a few, also collect astronomical amounts of data on their users . This data is then monetized by these companies for advertising campaigns and other practices to generate profits.
This is the economic model of Web2 and one of its fundamental problems. This is because users are not rewarded for sharing this valuable data . The only counterpart being the possibility of using services like Google or Facebook. It is a total surrender of control of personal data to the benefit of the giants of the Web.
The documentary The Social Dilemma distributed by Netflix perfectly illustrates this problem inherent in Web 2.0.
With the advent of blockchain technology, Web3 was able to emerge. In opposition to Web2 , this new Internet has the power to redistribute the cards.
What is Web 3?
Web 3 refers to decentralized applications and platforms developed and operating on public blockchains and sometimes backed by non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These are the famous dApps, whose underlying technology is the same as that of cryptocurrencies.
These dApps can therefore be developed on the Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot or BNB Chain blockchains. Web 3 is thus an Internet open to all, developed on the open source protocols of blockchain networks.
This definition is relatively vague and for good reason, Web 3 is being built . It is only in its infancy and at this stage, giving a precise definition is not easy. But let’s dive into the details to better understand what it is all about.
The very essence of Web 3.0 is composed of three main axes: decentralization, data control and confidentiality . This new paradigm is made possible by the blockchain, which offers a new method for storing data online with its distributed network and data encryption.
Decentralization in Web 3.0
Instead of the domination of centralized entities with strong decision-making power over Web 2.0, the management of Web 3.0 is entrusted to a distributed network of users such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
Participants in this new form of governance must collectively approve future updates, transactions or any operations.
Thus, blockchain dApps make it possible to decentralize the Internet and make it more fair, transparent, reliable and resistant to censorship . No central entity has the power to make a decision unilaterally and this is one of the greatest strengths of Web3.
Data control and confidentiality
The encryption of data stored on the blockchain implies very strict access to it . Consequently, only the individuals possessing the rights are able to consult them.
The decentralization of Web 3 also plays a very important role in controlling data through the distributed network .
It is a network on which a file containing data is shared on several servers, with solutions like Filecoin , a blockchain dedicated to decentralized data storage , on which anyone can store the data of other users.
On this network, every copy of a file must be identical , and if it is not, the data in that file becomes invalid.
Therefore, neither entity nor individual has the ability to access or change the data of a file without the permission of the person who owns it, or the agreement of the majority of the distributed network.
Another benefit comes from storage resiliency . Indeed, thanks to the distributed network, even if a server breaks down or ceases its activity, the data will still be accessible via other servers on which they are stored.
Here is a brief summary of what Web 3 brings compared to Web 2:
| Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 | |
| Servers | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Security | Guaranteed by companies | Guaranteed by the blockchain |
| User data | Companies are in control | The user is in control |
| Censorship | Possible, unilaterally | Censorship resistant |
| Content creation | Media addiction | No dependency |
| Ownership of Identity and Created Content | Companies | Users (NFTs, etc) |
| Access to services | With permission (from companies) | Without permission |
What does Web 3.0 bring?
Web 3 for content creators
With Web 3, content creators can express themselves the way they want without the fear of being censored unilaterally, like on Twitter or YouTube for example.
Important precision, a DAO can however collectively decide to censor an individual if it considers that it is necessary. However, it is a fairer governance and the abuse of censorship is much rarer thanks to decentralization, except in collusion by the participants of a DAO.
Another problem solved by Web 3 is the dependency of content creators on the centralized platforms on which they operate. Particularly in terms of remuneration, since only a tiny portion of the income generated by a creator is donated to him, the rest being recovered by the platform.
On Web3, since there are no intermediaries , creators are directly connected to their audience and create for them while they can benefit from a much higher income for their contributions.
The NFTs platform OpenSea , for example, charges a 2.5% fee for each transaction made on the platform, where the metaverse of Meta (a Web 2.0 application that tries to take on the appearance of Web 3.0) charges a commission of 47.5% on sales of NFTs.
Thus, creators migrating to Web 3.0 can potentially benefit from a more substantial income than on Web 2.0. This is particularly possible thanks to NFTs whose roles we will see in more detail in the next section.
Additionally, these decentralized networks do not have algorithms , which creators on Web2 depend on, that govern how content is seen by users. Ultimately, in Web 3.0, content creators actually own their audience and can be directly compensated by their actions.
The Web3 social networks, more commonly known as SocialFi (for Social Finance) will perhaps see their advent arrive in the near future and many projects are working on it, such as Lens Protocol by Aave.
Web 3 and non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
NFTs occupy a central place in the world of Web 3.0. Indeed, through this technology, it is possible to own a digital asset whose provenance and therefore its authenticity can be traced, since the NFT acts as a certificate of ownership and the transactions are visible on the blockchain.
Concretely, an NFT is an identifiable and unique digital unit stored on the blockchain . Thus, the complete history of previous owners can be consulted transparently thanks to the blockchain.
An NFT can also be sold or traded on the secondary market since a person holding an NFT has the right of ownership to it.
The applications of NFTs on the Web 3 are extremely numerous, some are well known such as video games with in-game objects that can become digital assets, or even in the field of digital art . But others are less known and yet these applications are the basis of the foundation of Web3.
Web 3.0 digital identity
Digital identity control is a crucial element on the Web3 in terms of decentralization and data confidentiality. There are several approaches to this.
While on the Web2 Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures or Google, Facebook and other accounts act as digital identities owned by these companies, on the Web3 it is possible to have your own digital identity thanks to NFTs .
Take the example of Ethereum Name Service (ENS), an open source protocol on the Ethereum blockchain that allows you to assign your digital identity to an Ethereum wallet .
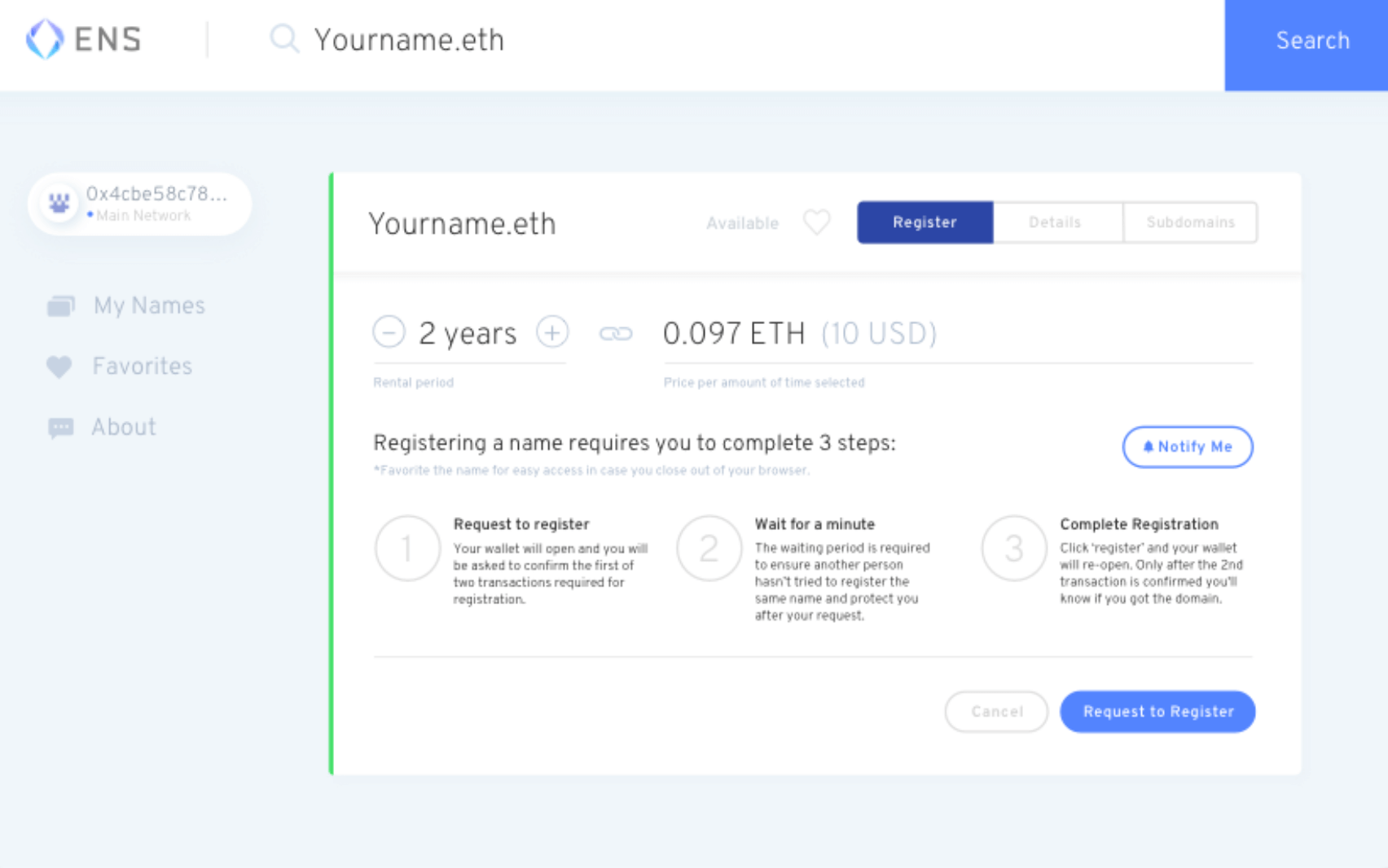
Figure 2: Overview of Ethereum Name Service (ENS)
Concretely, users can associate their Ethereum addresses, cryptographic hash or metadata with a name taking the following form: vitalik.eth. This name thus created is an NFT and can be used as a username on the Web3 . Note that each .eth address is unique, of course, and it is possible to sell or buy them on the secondary market.
These NFTs can be used as a credential to access a service, the difference being that the user has full control, rights and ownership over their digital identity.
It is about getting rid of centralized authentication systems through Web giants or traditional email addresses and passwords.
Another approach called Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) has emerged. With a focus on privacy protection and blockchain-based security interoperability. SSI removes the need to entrust personal information to a centralized entity and gives users complete control over what they share.
Finally, although at a very early stage at the time of writing these lines, the solution brought by Souls and soulbound tokens (SBTs) will potentially help users regain control of their identities.
Artists can certify via this digital identity that a created asset comes from them, for example. This is also to avoid the proliferation of malicious accounts or bots.
To conclude, the advantages are numerous, users become sole masters of their data on the Web3, which is no longer stored on centralized databases, but on distributed networks.
Metaverses and Web 3
Metaverses are a new iteration of the interface of the Internet . These are immersive digital spaces , with their own economy, and shared in which users can interact.
This vision of the future, of immersive worlds in which we will spend a lot of time interacting with others , working, having fun or even learning, is not yet concrete at the time of writing these lines.
Metaverses have the potential to combine many technologies : augmented reality, virtual reality, video games, social networks, cryptocurrencies, NFTs, etc.
Figure 3: Metaverse and Web3
This raises the question of data control and confidentiality . Many metaverses are under development, whether it’s The Sandbox, Decentraland, Otherside or even the metaverse project of Meta (formerly Facebook).
Web 3.0 can thus serve as the basis for metaverses to protect its users and provide decentralized applications that integrate perfectly with it, while metaverses can extend the vision of Web3 by developing virtual worlds where decentralized applications reign .
In this sense, both have a high complementarity potential by putting users at the center.
However, the success of this model is not yet guaranteed, since metaverses like those developed by centralized entities (Meta in particular) will probably keep the same data control scheme as on Web2, because it is the one of their main financial resources.
What are the limits of Web 3?
The promises of Web 3.0 may sound exciting, but there are also limitations despite the many benefits this new iteration of the Internet offers.
One of the first limitations concerns accessibility since it can have a cost. Owning an .eth address, for example, has a certain financial cost, while transactions on certain blockchains can apply exorbitant gas fees , which, for the moment, remains inaccessible for populations in less developed countries.
Another limit of Web 3.0 concerns the user experience since the technical barrier is always very high for the most neophytes. It is not yet possible to browse the Web3 without encountering technical difficulties for the average user.
The Web3 ecosystem is still very young and evolving very quickly. Therefore, it still depends a lot on centralized infrastructures to exist like GitHub, Discord, Twitter etc.
Many companies try to offer a Web3 alternative to these frameworks, but it may take time to establish itself as a viable alternative and none have emerged as a truly effective and intuitive solution.
Another limitation of Web 3.0 is the difficulty of regulating activities there . Seen as a positive point by some, it can also be a negative point since it can lead to an increase in cybercrime and other abuses.
However, it is necessary to temper these limitations , which are real at the time of writing these lines, but which could well be reduced as Web3 evolves.
Indeed, thanks to layer 2 solutions , to the evolution of the scalability of blockchains, to the development of increasingly simple protocols to use or even thanks to the DAOs managed in an efficient way by their members, the Web3 still has great potential to solve these problems .
Conclusion on Web 3
The Web 3 vision of a new, decentralized Internet emphasizing data control and privacy is gradually becoming a reality .
We are still in its infancy: it is estimated that in 2022 there will be as many individuals with an Ethereum address as there were Internet users in 1995.
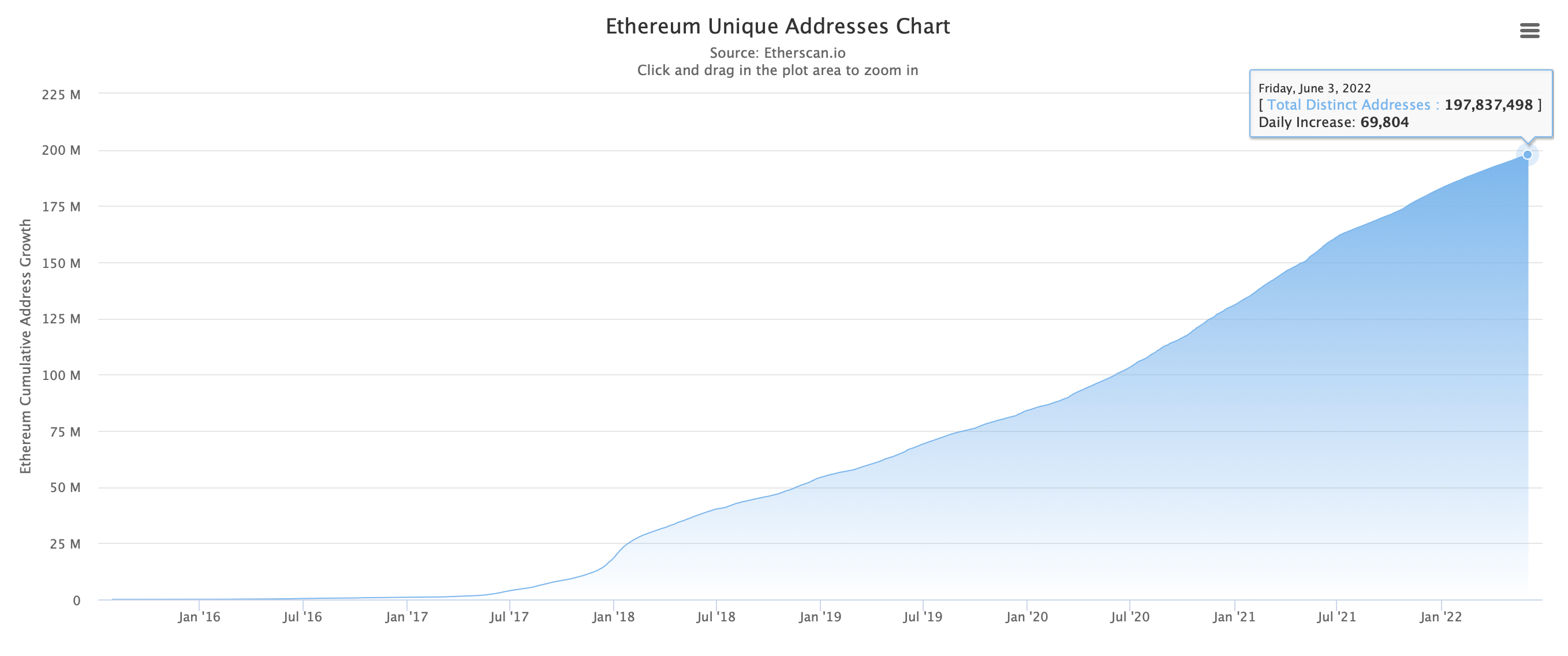
Figure 4: Number of unique Ethereum addresses
Many solutions attempting to replace Web2 entities have already been developed on Web3. While for web hosting on Web2, Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure reign supreme, Web3 has alternatives like InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and Skynet.
Regarding data storage , instead of the traditional Google Drive and Dropbox, Filecoin , Sia or Storj solutions are available on the Web3.
Internet browsers also have their Web3 alternatives with Brave or Opera Crypto Browser. Payments , naturally, can be made through wallets like MetaMask or TrustWallet.
Finally, although Web3 seems to be an inevitable revolution , the transition from Web2 to Web3 will probably take place over a relatively long time scale : it is estimated, given the current trend, that we would potentially reach 1 billion users on Web3 by 2031 (according to a16z).
One thing is certain, the way we interact with the Internet and other individuals will fundamentally change as this transition progresses.




